Mutations
MAPT K257T
Quick Links
Overview
Pathogenicity: Other Tauopathy : Pathogenic, Frontotemporal Dementia : Unclear Pathogenicity
Clinical
Phenotype: Tauopathy consistent with Pick's Disease
Reference Assembly: GRCh37/hg19
Position: Chr17:44073978 A>C
dbSNP ID: rs63750129
Coding/Non-Coding: Coding
DNA
Change: Substitution
Expected RNA
Consequence: Substitution
Expected Protein
Consequence: Missense
Codon
Change: AAG to ACG
Reference
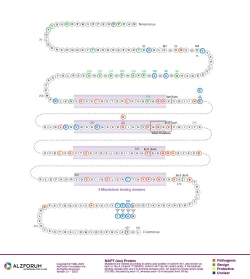
Isoform: Tau Isoform Tau-F (441 aa)
Genomic
Region: Exon 9
Findings
This mutation was identified in an individual from England with frontotemporal dementia who had neuropathologically confirmed Pick's disease. He developed symptoms at age 47 and died four years later. He presented first with memory decline and gradual changes in personality and behavior, namely disinhibition and erratic behavior. He also developed severe language impairments. He did not have a family history of dementia (his father died of myocardial infarction at age 79 and his mother died following a stroke at age 80). Segregation with disease could not be established, and it may be a de novo mutation (Rizzini et al., 2000; Pickering-Brown, 2000).
Neuropathology
Autopsy showed Pick’s disease, a subtype of FTD. Severe frontotemporal atrophy was observed, especially in the temporal lobes. Numerous tau-positive Pick bodies were seen in the neocortex, hippocampus, and some subcortical regions. Diffuse hyperphosphorylated tau was observed in some cell bodies (Rizzini et al., 2000).
Biological Effect
Recombinant tau protein with the K257T mutation showed reduced ability to promote microtubule assembly (Rizzini et al., 2000). In addition, in silico analyses predicted the mutation diminishes cathepsin cleavage which was confirmed in vitro using protease assays (Sampognaro et al., 2023). Consistent with these findings, the lysosomal degradation of mutant tau in neuronal-like SH-SY5Y cells was reduced.
Last Updated: 16 Jun 2023
References
Paper Citations
- Rizzini C, Goedert M, Hodges JR, Smith MJ, Jakes R, Hills R, Xuereb JH, Crowther RA, Spillantini MG. Tau gene mutation K257T causes a tauopathy similar to Pick's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2000 Nov;59(11):990-1001. PubMed.
- Pickering-Brown S, Baker M, Yen SH, Liu WK, Hasegawa M, Cairns N, Lantos PL, Rossor M, Iwatsubo T, Davies Y, Allsop D, Furlong R, Owen F, Hardy J, Mann D, Hutton M. Pick's disease is associated with mutations in the tau gene. Ann Neurol. 2000 Dec;48(6):859-67. PubMed.
- Sampognaro PJ, Arya S, Knudsen GM, Gunderson EL, Sandoval-Perez A, Hodul M, Bowles K, Craik CS, Jacobson MP, Kao AW. Mutations in α-synuclein, TDP-43 and tau prolong protein half-life through diminished degradation by lysosomal proteases. Mol Neurodegener. 2023 May 2;18(1):29. PubMed. Correction.
Further Reading
Learn More
Protein Diagram
Primary Papers
- Rizzini C, Goedert M, Hodges JR, Smith MJ, Jakes R, Hills R, Xuereb JH, Crowther RA, Spillantini MG. Tau gene mutation K257T causes a tauopathy similar to Pick's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2000 Nov;59(11):990-1001. PubMed.
- Pickering-Brown S, Baker M, Yen SH, Liu WK, Hasegawa M, Cairns N, Lantos PL, Rossor M, Iwatsubo T, Davies Y, Allsop D, Furlong R, Owen F, Hardy J, Mann D, Hutton M. Pick's disease is associated with mutations in the tau gene. Ann Neurol. 2000 Dec;48(6):859-67. PubMed.
Alzpedia
Disclaimer: Alzforum does not provide medical advice. The Content is for informational, educational, research and reference purposes only and is not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek advice from a qualified physician or health care professional about any medical concern, and do not disregard professional medical advice because of anything you may read on Alzforum.

Comments
No Available Comments
Make a Comment
To make a comment you must login or register.