Mutations
MAPT Q336R
Quick Links
Overview
Pathogenicity: Frontotemporal Dementia : Pathogenic
Clinical
Phenotype: Frontotemporal Dementia, Pick's disease
Reference Assembly: GRCh37/hg19
Position: Chr17:44095993 A>G
dbSNP ID: rs63750573
Coding/Non-Coding: Coding
DNA
Change: Substitution
Expected RNA
Consequence: Substitution
Expected Protein
Consequence: Missense
Codon
Change: CAG to CGG
Reference
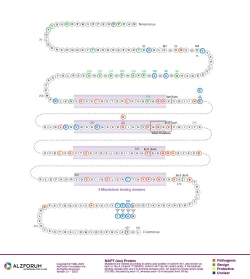
Isoform: Tau Isoform Tau-F (441 aa)
Genomic
Region: Exon 12
Findings
The proband was a 68‐year‐old man who died following a 10-year history of changes in memory, language, behavior, and personality. He had a family history of a similar dementing disorder, consistent with autosomal-dominant transmission. This mutation is thought to be pathogenic because it was identified in an individual with a clinical phenotype of frontotemporal dementia who had a family history of premature cognitive decline, although the genotypes of his affected family members are unknown, so pathogenicity could not be determined. The Q336R mutation was not found in 100 unaffected individuals (Pickering-Brown et al., 2004).
Neuropathology
Moderately severe atrophy of the frontal lobes and severe atrophy of the anterior temporal lobes, hippocampus, and amygdala were observed in the proband's brain. Although neuronal loss varied by region, in some areas neuronal loss and astrogliosis were extensive, leading to widespread spongiosis and loss of cytoarchitecture. Hyperphosphorylated tau accumulated in swollen (Pick) cells and intraneuronal inclusions (Pick bodies) were seen containing both three‐repeat (3R) and four‐repeat (4R) tau. Neurons within the frontal cortex contained neurofibrillary tangle‐like structures (both straight and twisted tubules), as well as Pick bodies in which the filaments were short and randomly oriented (Pickering-Brown et al., 2004).
Biological Effect
In vitro, the Q336R mutation enhanced tau filament assembly. Tau aggregation was preferentially increased for 3R isoforms. In addition, in contrast to most MAPT missense mutations, Q336R increased, rather than decreased, mutant tau's ability to promote microtubule assembly in both 3R and 4R isoforms (Pickering-Brown et al., 2004; Tacik et al., 2015).
Last Updated: 30 Oct 2015
References
Paper Citations
- Pickering-Brown SM, Baker M, Nonaka T, Ikeda K, Sharma S, Mackenzie J, Simpson SA, Moore JW, Snowden JS, de Silva R, Revesz T, Hasegawa M, Hutton M, Mann DM. Frontotemporal dementia with Pick-type histology associated with Q336R mutation in the tau gene. Brain. 2004 Jun;127(Pt 6):1415-26. Epub 2004 Mar 26 PubMed.
- Tacik P, DeTure M, Hinkle KM, Lin WL, Sanchez-Contreras M, Carlomagno Y, Pedraza O, Rademakers R, Ross OA, Wszolek ZK, Dickson DW. A Novel Tau Mutation in Exon 12, p.Q336H, Causes Hereditary Pick Disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2015 Nov;74(11):1042-52. PubMed.
Further Reading
Learn More
Protein Diagram
Primary Papers
- Pickering-Brown SM, Baker M, Nonaka T, Ikeda K, Sharma S, Mackenzie J, Simpson SA, Moore JW, Snowden JS, de Silva R, Revesz T, Hasegawa M, Hutton M, Mann DM. Frontotemporal dementia with Pick-type histology associated with Q336R mutation in the tau gene. Brain. 2004 Jun;127(Pt 6):1415-26. Epub 2004 Mar 26 PubMed.
Other mutations at this position
Alzpedia
Disclaimer: Alzforum does not provide medical advice. The Content is for informational, educational, research and reference purposes only and is not intended to substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek advice from a qualified physician or health care professional about any medical concern, and do not disregard professional medical advice because of anything you may read on Alzforum.

Comments
No Available Comments
Make a Comment
To make a comment you must login or register.